Introduction.
I was accepted into the Web3ladies cohort 3 mentorship program, and for the past few weeks, I've been learning the fundamentals of web3, blockchain, Ethereum, and other technologies. In this blog, I'll be sharing what I've learned so far.
The differences between Web 1, Web 2, and Web3.
Web 1
 What Exactly Is Web 1.0?
The original iteration of the Internet, known as Web 1.0, was developed by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and was the first global network to reflect the future of digital communications. It describes the initial "iteration" of what eventually developed into a platform with significant multi-functional applications.
The early Internet consisted largely of web pages connected by hyperlinks, lacking the modern-day extra images, controls, and forms. It was a "read-only" web or one that wasn't interactive in any meaningful way, according to experts. The majority of web users were passive, and most user inputs occurred offline. Individual webpages were often composed of static pages that were stored on free web hosting services or web servers maintained by internet service providers (ISPs).
What Exactly Is Web 1.0?
The original iteration of the Internet, known as Web 1.0, was developed by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and was the first global network to reflect the future of digital communications. It describes the initial "iteration" of what eventually developed into a platform with significant multi-functional applications.
The early Internet consisted largely of web pages connected by hyperlinks, lacking the modern-day extra images, controls, and forms. It was a "read-only" web or one that wasn't interactive in any meaningful way, according to experts. The majority of web users were passive, and most user inputs occurred offline. Individual webpages were often composed of static pages that were stored on free web hosting services or web servers maintained by internet service providers (ISPs).
Here are a few characteristics found in Web 1.0:
- It’s made up of static pages connected to a system via hyperlinks
- It has HTML 3.2 elements like frames and tables
- HTML forms get sent through e-mail
- The content comes from the server's filesystem, not a relational database management system
- It features GIF buttons and graphics
Web 2
 Web 2.0 refers to the second generation of the World Wide Web, which is centered on enabling online collaboration and information sharing. In its simplest form, Web 2.0 describes the shift away from static HTML Web pages and toward a more dynamic Web that is better organized and built around providing Web applications to users.
Web 2.0 refers to the second generation of the World Wide Web, which is centered on enabling online collaboration and information sharing. In its simplest form, Web 2.0 describes the shift away from static HTML Web pages and toward a more dynamic Web that is better organized and built around providing Web applications to users.
Here’s a breakdown of typical Web 2.0 characteristics:
- It offers free information sorting, allowing users to retrieve and classify data collectively
- It contains dynamic content that responds to the user’s input
- It employs Developed Application Programming Interfaces (API)
- It encourages self-usage and allows forms of interaction like:
- Podcasting
- Social media
- Blogging
- Commenting
- Web content voting
- It’s used by society at large and not limited to specific communities.
Web 3

The third generation of web technologies is known as Web 3.0 (Web3). The World Wide Web, commonly referred to as the web, serves as the basic building block of the internet by offering website and application services.
There isn't a single, accepted definition of Web 3.0 because it is continually changing and being defined. However, it is evident that Web 3.0 will heavily emphasize decentralized applications and utilize blockchain-based technology. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will both be used in Web 3.0 to enable smarter, more adaptive applications.
Here’s a list of typical Web 3.0 characteristics:
- It's a semantic web, where the web technology evolves into a tool that lets users create, share, and connect content via search and analysis.
- It is based on comprehension of words instead of numbers and keywords.
- It incorporates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. If these concepts are combined with Natural Language Processing (NLP), the result is a computer that uses Web 3.0 to become smarter and more responsive to user needs.
- It presents the connectivity of multiple devices and applications through the Internet of Things (IoT). Semantic metadata makes this process possible, allowing all available information to be effectively leveraged. In addition, people can connect to the Internet anytime, anywhere, without needing a computer or smart device.
- It offers users the freedom to interact publicly or privately without having an intermediary expose them to risks, therefore offering people “trustless” data.
- It uses 3-D graphics. In fact, we already see this in computer games, virtual tours, and e-commerce. It facilitates participation without needing authorization from a governing body. It’s permissionless.
- It can be used for:
- -Metaverses: A 3D-rendered, boundless, virtual world
- -Blockchain games: They allow users to have actual ownership of in-game resources, following the principles of NFTs
- Privacy and digital infrastructure: This use includes zero-knowledge proofs and more secure personal information
- -Decentralized finance. This use includes payment Blockchains, peer-to-peer digital financial transactions, smart contracts, and cryptocurrency Decentralized autonomous organizations. Community members own online communities.
The differences

From the aforementioned traits, it is simple to distinguish between web 1, web 2, and web 3.
Blockchain
 A blockchain is a shared distributed database or ledger between computer network nodes. A blockchain serves as an electronic database for storing data in digital form. The most well-known use of blockchain technology is for preserving a secure and decentralized record of transactions in cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin. The innovation of a blockchain is that it fosters confidence without the necessity for a reliable third party by ensuring the fidelity and security of a record of data.
A blockchain is a shared distributed database or ledger between computer network nodes. A blockchain serves as an electronic database for storing data in digital form. The most well-known use of blockchain technology is for preserving a secure and decentralized record of transactions in cryptocurrency systems like Bitcoin. The innovation of a blockchain is that it fosters confidence without the necessity for a reliable third party by ensuring the fidelity and security of a record of data.
The Function of a Blockchain
Blockchain aims to make it possible to share and record digital information without editing it. A blockchain serves as the basis for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be changed, removed, or destroyed. Blockchains are also referred to as Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT). The blockchain idea was first put forth as a research project in 1991, long before Bitcoin became a widely used application in 2009. Since then, the introduction of numerous cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts has led to explosive growth in the use of blockchains.
Features of Blockchain
1. Immutable
The blockchain is considered immutable if it cannot be changed and is thus a permanent network. For blockchain technology to work, nodes must be present. The digital ledger is replicated on every node in the network. Every node verifies a transaction's legality before adding it, and if the majority of nodes agree that it is valid, the transaction is added to the network. This means that no one may add any transaction blocks to the ledger without the consent of a majority of nodes. Any records that have been validated cannot be modified or reversed. As a result, no user on the network will be able to modify, alter, or remove it.
2. Distributed
For complete transparency, a copy of the ledger is available to all network users. A public ledger will give complete details on all users and transactions on the network. A better result is guaranteed by the spread of computational power among the machines. One of the key characteristics of blockchains is a distributed ledger for a variety of reasons, including: Since changes in a distributed ledger spread quickly, following what is happening in the ledger is simple. The ledger must be kept up to date, and every node on the blockchain network must take part in the validation. Due to the blockchain's lack of intermediaries, every change to the ledger will be updated in seconds or minutes. Other properties include:
3. Decentralized
4. Secure
5. Faster Settlement
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain.
Pros
Improved accuracy by removing human involvement in verification
Cost reductions by eliminating third-party verification
Decentralization makes it harder to tamper with
Transactions are secure, private, and efficient
Transparent technology
Provides a banking alternative and a way to secure personal information for citizens of countries with unstable or underdeveloped governments
Cons
Significant technology costs associated with mining bitcoin
Low transactions per second
History of use in illicit activities, such as on the dark web
Regulation varies by jurisdiction and remains uncertain
Data storage limitation
Blockchain and How it works
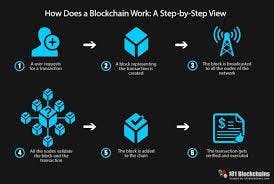
The functioning of the blockchain is dependent on three components: data, hash, and previous block hash.
Step 1:Data
The type of data stored in a block differs based on the blockchain. If the data is about Bitcoin, the blockchain maintains information about a transaction such as the sender, receiver, and transaction amount.
Step 2: hash
A hash, similar to a fingerprint, is also included in the block. When a block is created, its hash is computed. If something changes within the block, the hash will change as well. That is why hashing aids in detecting changes in a blockchain. If a block's fingerprint changes, it is no longer the same block.
Step 3: Previous data hash
A hash of a previous block is the final piece in a blockchain. The hash of the preceding block aids in the creation of a chain, and as a result of these aspects, the blockchain is extremely secure to trust and use. In a blockchain, each block is linked to the previous hash's data, but if any of the blocks' data is tampered with, the hash changes instantly, and the subsequent block recognizes it and makes the changes immediately.
Computers nowadays are capable of storing hundreds of thousands of hashes each second. To make the blockchain valid again, the hash of tampered blocks is altered by default, as are the hashes of other blocks. This is accomplished with the assistance of proof of work that has been discussed above.
Ethereum and Bitcoin

Ethereum
Ethereum is a blockchain-based decentralized global software platform at its heart. It is well known for ether, often known as ETH, which is its native cryptocurrency.
Anyone can use Ethereum to develop any secure digital technology. There is a token built into it specifically for usage on the blockchain network, but users may also use it to pay for tasks done on the blockchain.

Scalable, programmable, secure, and decentralized are all features of Ethereum. It is the blockchain of choice for businesses and developers who are building technology on top of it to transform several sectors and how we live our daily lives.
Bitcoin
The first and most well-known cryptocurrency is called Bitcoin. Through the use of a decentralized protocol, cryptography, and a means to reach international consensus on the status of a regularly updated public transaction record known as a "blockchain," it permits peer-to-peer exchange of value in the digital sphere.
 The digital currency known as bitcoin has a known monetary policy that is arguably unchangeable can be transmitted internationally without requiring a centralized middleman and exists outside of any government, state, or financial institution.
The digital currency known as bitcoin has a known monetary policy that is arguably unchangeable can be transmitted internationally without requiring a centralized middleman and exists outside of any government, state, or financial institution.
Bitcoin can be viewed as a political, philosophical, and economic system on a deeper level. This is because of how many technical elements it incorporates, how many actors and stakeholders it engages, and how the protocol modification process works.
Both the monetary unit known as Bitcoin and the Bitcoin software protocol, both of which have the ticker symbol BTC, are referred to as "Bitcoin.
Smart Contracts
 Simply put, smart contracts are blockchain-based algorithms that execute when certain criteria are met. They are often used to automate the implementation of an agreement so that all parties can be certain of the conclusion right away, without the need for an intermediary or additional delay. They can also automate a workflow such that when circumstances are met, the following action is executed.
Simply put, smart contracts are blockchain-based algorithms that execute when certain criteria are met. They are often used to automate the implementation of an agreement so that all parties can be certain of the conclusion right away, without the need for an intermediary or additional delay. They can also automate a workflow such that when circumstances are met, the following action is executed.
How smart contracts work
Smart contracts work by following simple “if/when…then…” statements that are written into code on a blockchain. A network of computers executes the actions when predetermined conditions have been met and verified. These actions could include releasing funds to the appropriate parties, registering a vehicle, sending notifications, or issuing a ticket. The blockchain is then updated when the transaction is completed. That means the transaction cannot be changed, and only parties who have been granted permission can see the results.
Within a smart contract, there can be as many stipulations as needed to satisfy the participants that the task will be completed satisfactorily. To establish the terms, participants must determine how transactions and their data are represented on the blockchain, agree on the “if/when...then…” rules that govern those transactions, explore all possible exceptions, and define a framework for resolving disputes.
Then the smart contract can be programmed by a developer – although increasingly, organizations that use blockchain for business provide templates, web interfaces, and other online tools to simplify structuring smart
Benefits of smart contracts
Speed, efficiency, and accuracy Once a condition is met, the contract is executed immediately. Because smart contracts are digital and automated, there’s no paperwork to process and no time spent reconciling errors that often result from manually filling in documents.
Trust and transparency Because there’s no third party involved, and because encrypted records of transactions are shared across participants, there’s no need to question whether information has been altered for personal benefit.
-Security Blockchain transaction records are encrypted, which makes them very hard to hack. Moreover, because each record is connected to the previous and subsequent records on a distributed ledger, hackers would have to alter the entire chain to change a single record.
- Savings Smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries to handle transactions and, by extension, their associated time delays and fees.
DApps
 Decentralized applications (dApps) are digital applications or programs that exist and run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers instead of a single computer. DApps (also called "apps") are outside the purview and control of a single authority. DApps—which are often built on the Ethereum platform—can be developed for a variety of purposes including gaming, finance, and social media.
Decentralized applications (dApps) are digital applications or programs that exist and run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers instead of a single computer. DApps (also called "apps") are outside the purview and control of a single authority. DApps—which are often built on the Ethereum platform—can be developed for a variety of purposes including gaming, finance, and social media.
Ethereum mining
 Mining is the process of creating a block of transactions to be added to the Ethereum blockchain.
Mining is the process of creating a block of transactions to be added to the Ethereum blockchain.
The word mining originates in the context of the gold analogy for crypto currencies. Gold or precious metals are scarce, and so are digital tokens, and the only way to increase the total volume is through mining. This is appropriate to the extent that in Ethereum too, the only mode of issuance post launch is via mining. Unlike these examples, however, mining is also the way to secure the network by creating, verifying, publishing, and propagating blocks in the blockchain.
Mining ether = Securing the Network
Ethereum, like Bitcoin, currently uses a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism. Mining is the lifeblood of proof-of-work. Ethereum miners - computers running software - use their time and computation power to process transactions and produce blocks.
Conclusion
One of my favorite aspects of Web3ladies' teaching methodology is that we are provided with lesson materials that we can utilize to continue learning and conducting research even after class. These are some of the new things I discovered while in this pre-prep phase of Web3ladies cohort 3, and I look forward to discovering more in the future.

